Learn TypeScript
Emitting source maps
Emitting source maps
In this lesson, we will learn how to generate source maps for transpiled code so that it can be debugged.
Technical requirements
You will need the following installed on your computer for this lesson:
Node.js and npm. You can download these from https://nodejs.org/en/download. If you already have these installed, make sure that Node.js is at least version 8.2, and that npm is at least version 5.
Code editor such as Visual Studio Code. This can be installed from https://code.visualstudio.com.
The starter project which can be found here.
After the starter project has been downloaded. Open it in Visual Studio Code and execute the following command in a Terminal window:
npm installThis will install the project dependency, which is TypeScript.
Generating source map files
Source maps enable us to debug TypeScript code. A source map file maps from the transpiled JavaScript file to the original TypeScript file. This allows the original TypeScript code to be reconstructed while debugging.
We can generate a basic source map using the sourceMap compilation option.
The code in the starter project is a nodejs program that contains a debugger statement in index.ts.
- Add the following to
tsconfig.json:
{ "compilerOptions": { ... "sourceMap": true }, ...}Open the
index.tsfile in thesrcfolder.Go to the run view in Visual Studio Code by clicking the Run icon in the activity bar, which is on the left-hand side.
👉Click Run and Debug in the panel that appears.
Select Node.js from the list that appears.
The code is compiled, and the debugger starts. The execution breaks on the debugger statement:
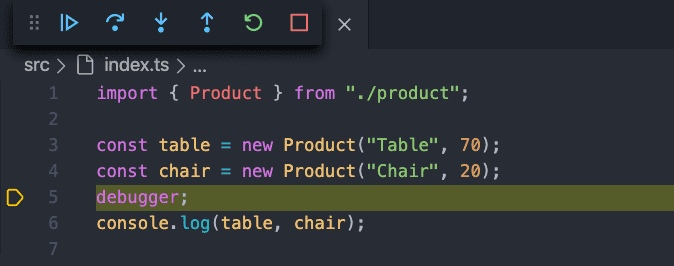
Are we seeing the TypeScript code in the debug window or the transpiled JavaScript code?
Nice!
Stop the debugger by clicking the red square icon.
Look in the
distfolder and notice themapfiles. These are the source maps.Open a source map file which is in JSON format:
{ "version": 3, "file": "index.js", "sourceRoot": "", "sources": [ "../src/index.ts" ], "names": [], "mappings": ";;AAAA,uCAAoC;....""}`}Here are some key points about the source map:
The reference to the JavaScript file is defined in a
filefield.The reference to the TypeScript file is in a
sourcesfield. Notice that it references the file in the project structure.The
sourceRootfield is the root path of the TypeScript files.The
versionfield defines which version of the source map spec is being used.The
namesfield is a list of identifiers used in the source code that were changed or removed from the output.The
mappingsfield contains mappings for every position in the JavaScript code back to positions in the TypeScript code. These are base64 encoded variable-length quantities.Open a JavaScript file. Notice the comment at the bottom of it:
//# sourceMappingURL=index.js.mapThis is the reference to the source map.
- Remove
"sourceMap": truefromtsconfig.jsonand delete thedistfolder before continuing to the next section.
Including source maps in generated JavaScript
There is a compilation option called inlineSourceMap that will put the source map inside the transpiled JavaScript file.
Let's explore this.
- Add the following to
tsconfig.json:
{ "compilerOptions": { ... "inlineSourceMap": true }, ...}- Run the TypeScript compiler:
npm run tscWhere are the source maps?
- Remove
"inlineSourceMap": truefromtsconfig.jsonand delete thedistfolder before continuing to the next section.
Including TypeScript code in source maps
By default, the TypeScript code isn't included in the generated source maps. Instead, the source maps reference the TypeScript code in the project. This is fine for local development, but not ideal if you are trying to debug a problem when the code has been deployed to a web server. We can use the inlineSources option to change this behavior.
- Add the following to
tsconfig.json:
{ "compilerOptions": { ... "sourceMap": true, "inlineSources": true }, ...}The inlineSources option can be used with sourceMap or inlineSourceMap.
- Rerun the TypeScript compiler:
npm run tscHow is the TypeScript code referenced in the source maps now?
Cool!
- Delete the
distfolder before continuing to the next section.
Changing the location of source maps
By default, the transpiled JavaScript expects source maps to be in the same directory. The behavior can be changed with the mapRoot option.
- Add the following to
tsconfig.json:
{ "compilerOptions": { ... "mapRoot": "maps" }, ...}- Rerun the TypeScript compiler:
npm run tscWhere are the source maps located?
- Open a JavaScript file and look at source map reference at the bottom.
//# sourceMappingURL=../src/maps/index.js.mapThe source map is now expected to be in a maps folder.
- Remove
"mapRoot": "maps"and"inlineSources": truefromtsconfig.jsonand delete thedistfolder before continuing to the next section.
Changing the source map reference for TypeScript code
As mentioned earlier, the source maps reference the TypeScript code in the project structure by default. The location of the TypeScript code can be changed using a sourceRoot option.
- Add the following to
tsconfig.json:
{ "compilerOptions": { ... "sourceMap": true, "sourceRoot": "ts" }, ...}- Rerun the TypeScript compiler:
npm run tscThe sourceRoot field within the source map is now updated with the path we specified.
{ ... "sourceRoot":"ts/", ...}Summary
Source maps allow TypeScript code to be debugged and can be switched on using the sourceMap or inlineSourceMap options.
inlineSources is useful when debugging code on a deployed server.
mapRoot is useful with sourceMap when debugging code on a deployed server, and the map files aren't next to the JavaScript files.
sourceRoot is useful with sourceMap when debugging code on a deployed server, and the TypeScript files are in a different relative location to the local project.
In the next lesson, we will learn how to specify what standard TypeScript libraries are used during type checking.